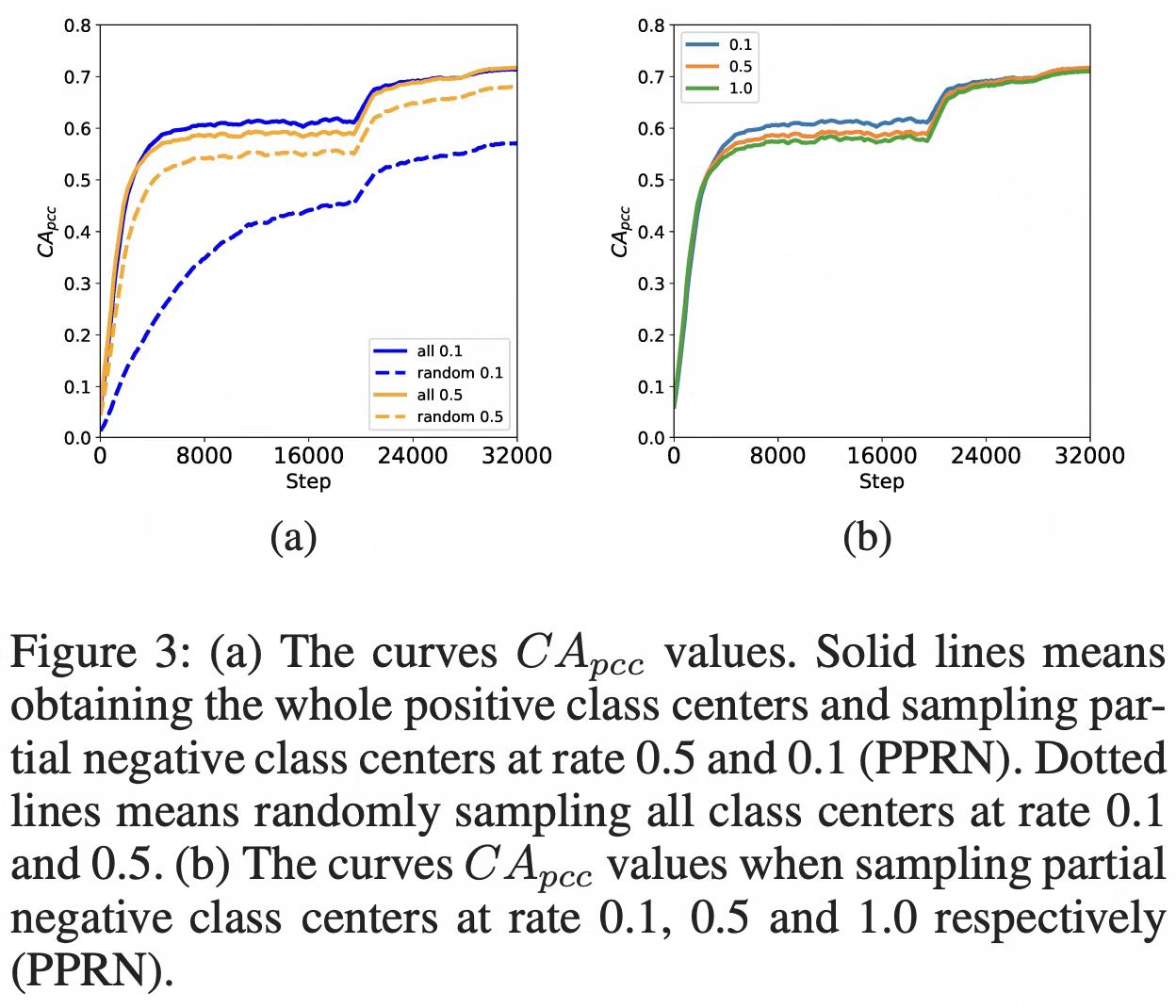
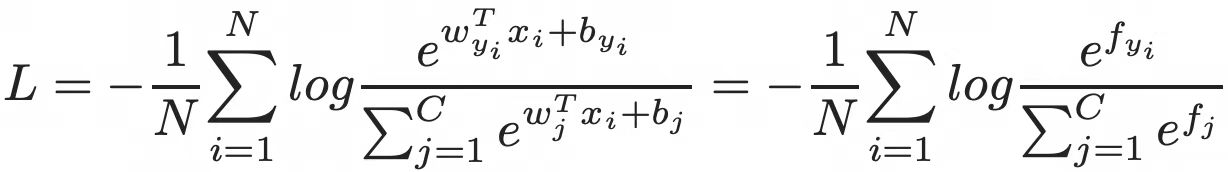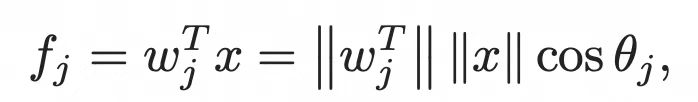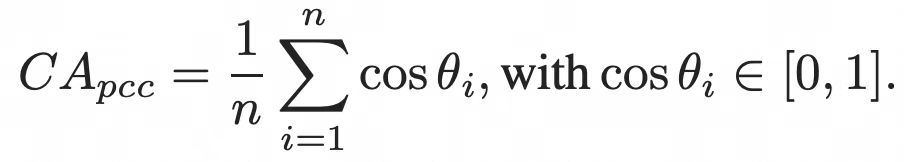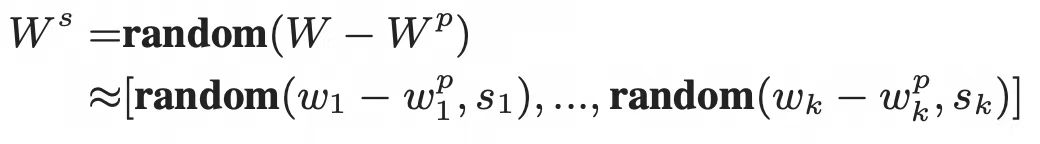1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
| import math
from typing import Callable
import torch
from torch import distributed
from torch.nn.functional import linear, normalize
class PartialFC_V2(torch.nn.Module):
"""
https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.15565
A distributed sparsely updating variant of the FC layer, named Partial FC (PFC).
When sample rate less than 1, in each iteration, positive class centers and a random subset of
negative class centers are selected to compute the margin-based softmax loss, all class
centers are still maintained throughout the whole training process, but only a subset is
selected and updated in each iteration.
.. note::
When sample rate equal to 1, Partial FC is equal to model parallelism(default sample rate is 1).
Example:
--------
>>> module_pfc = PartialFC(embedding_size=512, num_classes=8000000, sample_rate=0.2)
>>> for img, labels in data_loader:
>>> embeddings = net(img)
>>> loss = module_pfc(embeddings, labels)
>>> loss.backward()
>>> optimizer.step()
"""
_version = 2
def __init__(
self,
margin_loss: Callable,
embedding_size: int,
num_classes: int,
sample_rate: float = 1.0,
fp16: bool = False,
):
"""
Paramenters:
-----------
embedding_size: int
The dimension of embedding, required
num_classes: int
Total number of classes, required
sample_rate: float
The rate of negative centers participating in the calculation, default is 1.0.
"""
super(PartialFC_V2, self).__init__()
assert (
distributed.is_initialized()
), "must initialize distributed before create this"
self.rank = distributed.get_rank()
self.world_size = distributed.get_world_size()
self.dist_cross_entropy = DistCrossEntropy()
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.sample_rate: float = sample_rate
self.fp16 = fp16
self.num_local: int = num_classes // self.world_size + int(
self.rank < num_classes % self.world_size
)
self.class_start: int = num_classes // self.world_size * self.rank + min(
self.rank, num_classes % self.world_size
)
self.num_sample: int = int(self.sample_rate * self.num_local)
self.last_batch_size: int = 0
self.is_updated: bool = True
self.init_weight_update: bool = True
self.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.normal(0, 0.01, (self.num_local, embedding_size)))
if isinstance(margin_loss, Callable):
self.margin_softmax = margin_loss
else:
raise
def sample(self, labels, index_positive):
"""
This functions will change the value of labels
Parameters:
-----------
labels: torch.Tensor
pass
index_positive: torch.Tensor
pass
optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer
pass
"""
with torch.no_grad():
positive = torch.unique(labels[index_positive], sorted=True).cuda()
if self.num_sample - positive.size(0) >= 0:
perm = torch.rand(size=[self.num_local]).cuda()
perm[positive] = 2.0
index = torch.topk(perm, k=self.num_sample)[1].cuda()
index = index.sort()[0].cuda()
else:
index = positive
self.weight_index = index
labels[index_positive] = torch.searchsorted(index, labels[index_positive])
return self.weight[self.weight_index]
def forward(
self,
local_embeddings: torch.Tensor,
local_labels: torch.Tensor,
):
"""
Parameters:
----------
local_embeddings: torch.Tensor
feature embeddings on each GPU(Rank).
local_labels: torch.Tensor
labels on each GPU(Rank).
Returns:
-------
loss: torch.Tensor
pass
"""
local_labels.squeeze_()
local_labels = local_labels.long()
batch_size = local_embeddings.size(0)
if self.last_batch_size == 0:
self.last_batch_size = batch_size
assert self.last_batch_size == batch_size, (
f"last batch size do not equal current batch size: {self.last_batch_size} vs {batch_size}")
_gather_embeddings = [
torch.zeros((batch_size, self.embedding_size)).cuda()
for _ in range(self.world_size)
]
_gather_labels = [
torch.zeros(batch_size).long().cuda() for _ in range(self.world_size)
]
_list_embeddings = AllGather(local_embeddings, *_gather_embeddings)
distributed.all_gather(_gather_labels, local_labels)
embeddings = torch.cat(_list_embeddings)
labels = torch.cat(_gather_labels)
labels = labels.view(-1, 1)
index_positive = (self.class_start <= labels) & (
labels < self.class_start + self.num_local
)
labels[~index_positive] = -1
labels[index_positive] -= self.class_start
if self.sample_rate < 1:
weight = self.sample(labels, index_positive)
else:
weight = self.weight
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(self.fp16):
norm_embeddings = normalize(embeddings)
norm_weight_activated = normalize(weight)
logits = linear(norm_embeddings, norm_weight_activated)
if self.fp16:
logits = logits.float()
logits = logits.clamp(-1, 1)
logits = self.margin_softmax(logits, labels)
loss = self.dist_cross_entropy(logits, labels)
return loss
class DistCrossEntropyFunc(torch.autograd.Function):
"""
CrossEntropy loss is calculated in parallel, allreduce denominator into single gpu and calculate softmax.
Implemented of ArcFace (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.07698v1.pdf):
"""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, logits: torch.Tensor, label: torch.Tensor):
""" """
batch_size = logits.size(0)
max_logits, _ = torch.max(logits, dim=1, keepdim=True)
distributed.all_reduce(max_logits, distributed.ReduceOp.MAX)
logits.sub_(max_logits)
logits.exp_()
sum_logits_exp = torch.sum(logits, dim=1, keepdim=True)
distributed.all_reduce(sum_logits_exp, distributed.ReduceOp.SUM)
logits.div_(sum_logits_exp)
index = torch.where(label != -1)[0]
loss = torch.zeros(batch_size, 1, device=logits.device)
loss[index] = logits[index].gather(1, label[index])
distributed.all_reduce(loss, distributed.ReduceOp.SUM)
ctx.save_for_backward(index, logits, label)
return loss.clamp_min_(1e-30).log_().mean() * (-1)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, loss_gradient):
"""
Args:
loss_grad (torch.Tensor): gradient backward by last layer
Returns:
gradients for each input in forward function
`None` gradients for one-hot label
"""
(
index,
logits,
label,
) = ctx.saved_tensors
batch_size = logits.size(0)
one_hot = torch.zeros(
size=[index.size(0), logits.size(1)], device=logits.device
)
one_hot.scatter_(1, label[index], 1)
logits[index] -= one_hot
logits.div_(batch_size)
return logits * loss_gradient.item(), None
class DistCrossEntropy(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(DistCrossEntropy, self).__init__()
def forward(self, logit_part, label_part):
return DistCrossEntropyFunc.apply(logit_part, label_part)
class AllGatherFunc(torch.autograd.Function):
"""AllGather op with gradient backward"""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, tensor, *gather_list):
gather_list = list(gather_list)
distributed.all_gather(gather_list, tensor)
return tuple(gather_list)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, *grads):
grad_list = list(grads)
rank = distributed.get_rank()
grad_out = grad_list[rank]
dist_ops = [
distributed.reduce(grad_out, rank, distributed.ReduceOp.SUM, async_op=True)
if i == rank
else distributed.reduce(
grad_list[i], i, distributed.ReduceOp.SUM, async_op=True
)
for i in range(distributed.get_world_size())
]
for _op in dist_ops:
_op.wait()
grad_out *= len(grad_list)
return (grad_out, *[None for _ in range(len(grad_list))])
|